TL;DR
How the Hypertension Feature Works
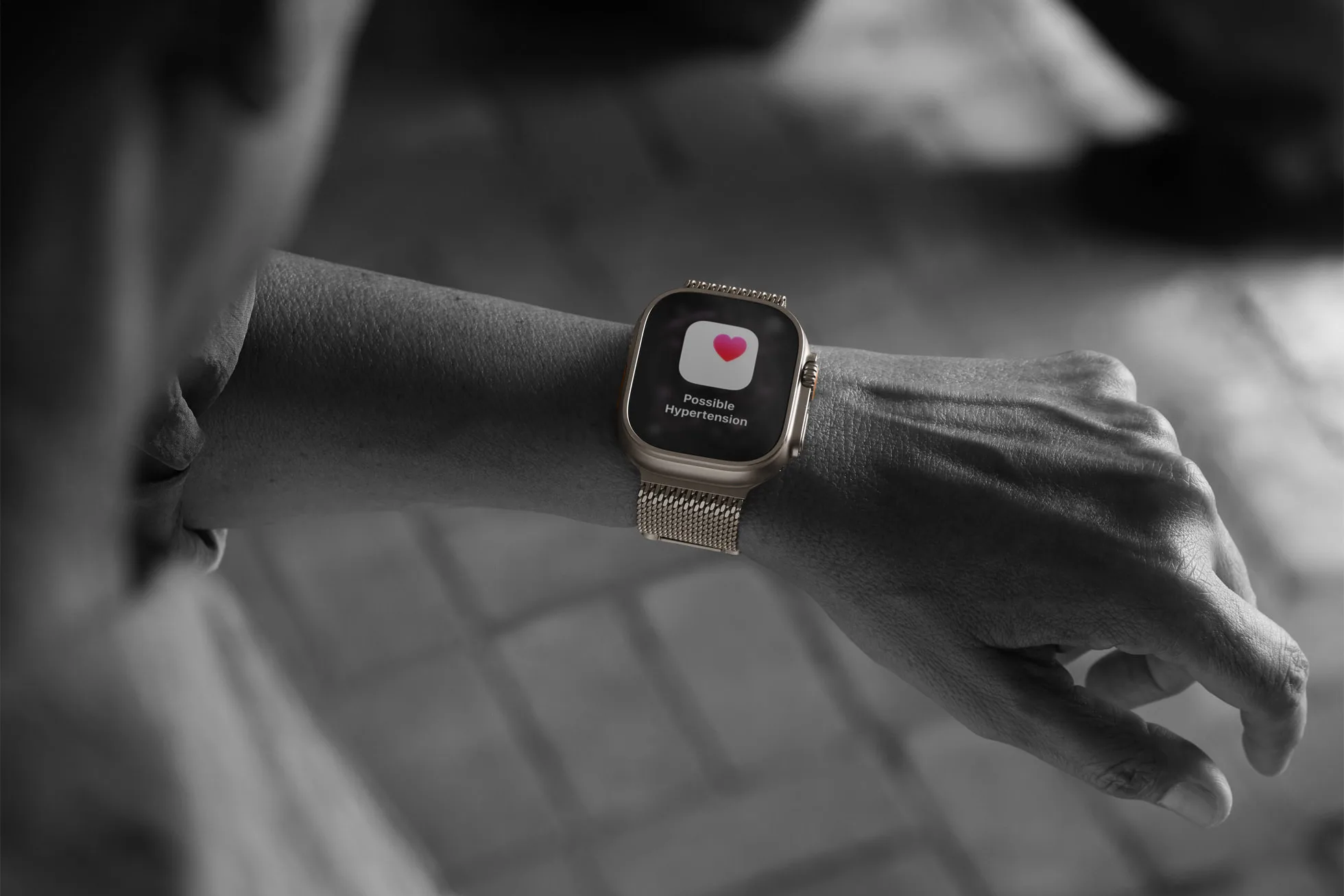
Apple Watch doesn't measure blood pressure directly—there's no cuff involved. Instead, it uses the optical heart sensor (the same one that tracks your heart rate) to analyze subtle patterns in your pulse waveform over time.
The feature works by collecting data passively in the background. Over a 30-day period, the watch analyzes this data using machine learning algorithms trained on clinical studies. When it detects patterns consistent with elevated blood pressure, it sends you a notification.
Compatible Devices
- Apple Watch Ultra 3
- Apple Watch Series 10
- Apple Watch Series 9 (with watchOS 12+)
What a Hypertension Notification Means
A hypertension notification from Apple Watch is a screening alert, not a diagnosis. It means the watch has detected patterns that warrant further investigation. Think of it like a check engine light—it's telling you something might need attention, but you need more information to know for sure.
Important
What to Do If You Get a Notification
Step 1: Don't Panic
The notification is designed to encourage you to check your blood pressure, not to cause alarm. Many people who receive notifications may not actually have hypertension.
Step 2: Get a Blood Pressure Monitor
If you don't already have one, get a validated upper arm blood pressure monitor. The American Heart Association maintains a list of validated devices. Avoid wrist monitors for this purpose— upper arm cuffs are more accurate.
Step 3: Track for One Week
Take your blood pressure twice daily—once in the morning before medication or caffeine, and once in the evening. Record all readings. This gives you and your doctor a clear picture of your actual blood pressure patterns.
Step 4: Share with Your Doctor
Bring your week of readings to your doctor. Apps like Cardilog can generate professional PDF reports that make it easy to share your data. Your doctor will review the readings and determine if further evaluation or treatment is needed.
Understanding Blood Pressure Numbers
Blood pressure is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and expressed as two numbers:
- Systolic (top number): Pressure when your heart beats
- Diastolic (bottom number): Pressure when your heart rests between beats
Here's what the numbers mean:
- Normal: Less than 120/80 mmHg
- Elevated: 120-129/less than 80 mmHg
- High Blood Pressure Stage 1: 130-139/80-89 mmHg
- High Blood Pressure Stage 2: 140+/90+ mmHg
Why This Feature Matters
Hypertension is often called the "silent killer" because it typically has no symptoms until it causes serious damage. Nearly half of American adults have high blood pressure, and many don't know it.
By providing passive, continuous screening, Apple Watch can help identify people who should get their blood pressure checked—potentially catching hypertension before it leads to heart disease, stroke, or kidney problems.
Limitations to Keep in Mind
- The feature is designed for people over 18 who haven't been diagnosed with hypertension
- It may not detect all cases of high blood pressure
- It cannot replace regular blood pressure monitoring
- False positives can occur
- The algorithm requires 30 days of data before it can provide an assessment